Table Of Contents
Environmental Impact
Heat pumps are often lauded for their efficiency in heating and cooling spaces, yet their environmental impact cannot be overlooked. One critical aspect to consider is the use of refrigerants. Many heat pumps utilise hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which can have a significant greenhouse gas effect if released into the atmosphere. Although newer models are increasingly incorporating more environmentally friendly alternatives, the transition is gradual, leaving older systems potentially harmful to the climate.
Another factor is the source of electricity used to power heat pumps. In areas like Heat Pump Aston, Birmingham, where the electricity grid may still rely on fossil fuels, the overall reduction in emissions from using a heat pump can be diminished. If the energy input comes from non-renewable sources, the environmental benefits of the system can be substantially reduced. This dependence on the electricity supply presents a wider challenge in evaluating the true sustainability of heat pumps.
More tips and tricks can be found here.
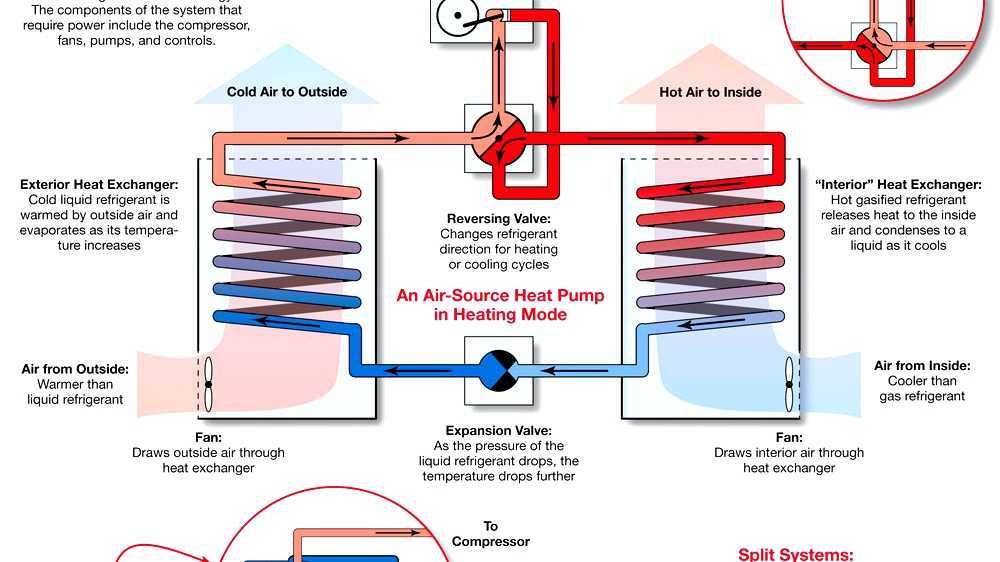
Assessing the Use of Refrigerants
Refrigerants play a crucial role in the operation of heat pumps. While modern refrigerants are designed to be more environmentally friendly than their predecessors, concerns still linger regarding their overall impact. Some fluids contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if leaks occur during maintenance or operation. This factor is particularly significant in urban areas, such as those featuring services like Heat Pump Digbeth, Birmingham, where the concentration of systems can amplify potential risks.
Regulations surrounding the use of refrigerants continue to evolve in an effort to mitigate these concerns. Industry standards demand careful handling and disposal of these substances to minimise environmental harm. Despite advancements, the possibility of unexpected leaks remains, underscoring the need for rigorous monitoring processes. Increased awareness and proactive measures can help ensure the responsible use of refrigerants within the growing heat pump market.
Energy Source Dependency
The performance of heat pumps is heavily reliant on the energy sources used for electricity generation. In markets where electricity is produced predominantly from fossil fuels, the environmental advantages of heat pumps diminish significantly. This dependency on the energy mix of a region can dramatically influence both carbon emissions and operational costs, making it crucial for homeowners to consider the sustainability of their electricity supply. For residents in areas like Heat Pump Handsworth Wood, Birmingham, understanding the local energy landscape is essential for evaluating the long-term benefits and drawbacks of heat pump installation.
Additionally, the shifting dynamics of the energy market can create challenges for heat pump users. Variations in electricity prices can impact the overall cost-effectiveness of operating a heat pump, potentially leading to higher energy bills during peak demand periods. Homeowners must remain vigilant about these fluctuations, as they can negate some of the economic advantages associated with heat pumps. Furthermore, this instability can influence the decision-making process for those considering the transition to heat pump technology in Heat Pump Handsworth Wood, Birmingham.
Potential Risks of Electricity Price Fluctuations
The reliance on electricity to operate heat pumps introduces a vulnerability to fluctuations in electricity prices. In areas like Heat Pump Gay Village, Birmingham, this can lead to unpredictable heating costs, especially during peak demand periods. As prices rise, homeowners may find their energy bills increasing substantially, which can deter some from adopting this technology.
Furthermore, since heat pumps typically consume more electricity during colder months, households could face financial strain if prices spike during winter when heating needs are at their highest. This dependence on electric supply can lead to concerns over both budgeting for energy expenses and the long-term feasibility of maintaining year-round comfort without incurring excessive costs.
Limited Heating Capacity
Heat pumps are designed to operate efficiently within a specific temperature range. While they excel in moderate climates, their capacity to deliver adequate heating diminishes significantly in extremely cold conditions. During periods of severe frost or heavy snowfall, the heat pump may struggle to extract sufficient heat from the outside air, which can lead to inadequate indoor warmth. This limitation can be particularly concerning for homeowners in regions known for harsh winters.
In areas like Gay Village, Birmingham, where winter temperatures can drop unexpectedly, relying solely on a heat pump may not provide the necessary comfort. Many users might need to consider supplementary heating options to ensure a consistent and comfortable indoor environment. This can result in increased energy costs and complicate the overall efficiency of the heating system. Additionally, the initial expectation of sustained performance might not align with the reality of extreme weather challenges.
Suitability for Extremely Cold Climates
Heat pumps are designed to operate efficiently within a specific temperature range. In extremely cold climates, their performance may decline, leading to less effective heating. As the outdoor temperature drops, the heat pump must work harder to extract heat from the air, which can result in diminished efficiency. In areas with frequent and severe cold snaps, relying solely on a heat pump can lead to inadequate indoor temperatures, necessitating additional heating systems for comfort.
In regions like the Heat Pump Colmore Business District, Birmingham, the climate may not consistently reach the extremes seen in colder locales, making heat pumps a viable option. However, homeowners and businesses must consider local weather patterns and potential fluctuations to ensure the chosen system can handle occasional cold spells. Properly assessing insulation and energy needs becomes crucial in determining if a heat pump will meet the demands of such environments.
FAQS
What are the main environmental concerns associated with heat pumps?
The primary environmental concerns relate to the use of refrigerants in heat pumps, which can have global warming potential if leaked. Additionally, the source of electricity used to power the heat pump can impact its overall carbon footprint.
How do refrigerants affect the environment when using a heat pump?
Some refrigerants used in heat pumps can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if they escape into the atmosphere. It's essential to choose heat pumps that utilise environmentally friendly refrigerants to minimise this impact.
What are the energy source dependencies of heat pumps?
Heat pumps rely on electricity to operate, making them dependent on the local energy grid. If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, it can negate some of the environmental benefits associated with heat pumps.
How can electricity price fluctuations impact the efficiency of heat pumps?
Fluctuations in electricity prices can affect the overall running costs of heat pumps. If electricity prices rise significantly, it may reduce the cost-effectiveness of using a heat pump for heating.
Are heat pumps suitable for use in extremely cold climates?
Heat pumps may struggle to provide adequate heating in extremely cold climates, as their efficiency decreases at lower temperatures. In such cases, supplementary heating systems may be necessary to ensure comfort.




